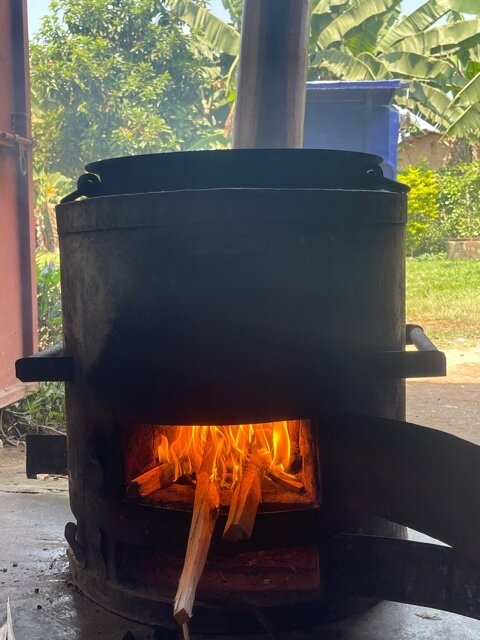
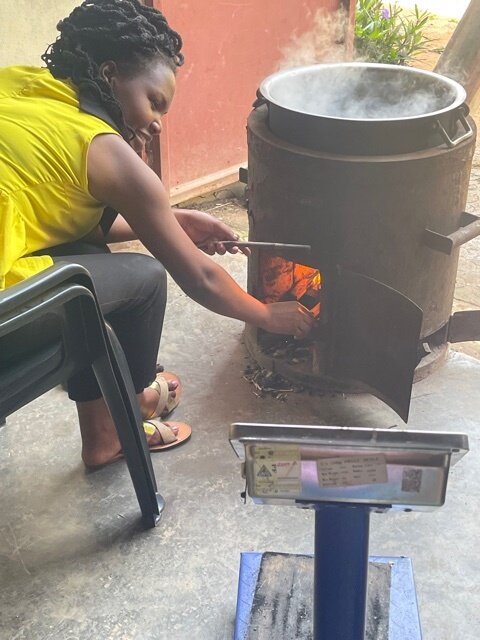
July has been a busy month for testing, as twelve institutional improved cook stoves (IICS) of 30 litres capacity that have been in operation since 2016, have been collected from different schools within Kampala and brought to our offices to perform the Water Boiling Test.
The Water Boiling Test (WBT) is a simplified simulation of the cooking process. It is intended to measure how efficiently a stove uses fuel to heat water in a cooking pot and the quantity of emissions produced while cooking.
The Water Boiling Test was developed to assess stove performance in a controlled manner. It is an approximation of the cooking process and is conducted in controlled conditions by trained technicians.
The WBT test for efficiency can be performed with simple equipment, always ensuring it has been previously calibrated by the Uganda National Bureau of Standards. (If emissions are measured, more complex equipment is required.) Such tests are mandatory to run, annually, under Simoshi’s registered Project Activity “Institutional Improved Cook Stoves for Schools and Institutions in Uganda”, to ensure the disseminated project IICS are still achieving at least 50% of fuel savings when compared to the baseline stoves/3-stone fires locally used. Its primary benefits are:
Provide initial or laboratory assessments of stove performance in a controlled setting
Compare the effectiveness of different designs at performing similar tasks
Evaluate stove changes during development
Select the most promising products for field trials
Ensure that manufactured stoves meet intended performance based on designs throughout their lifetime